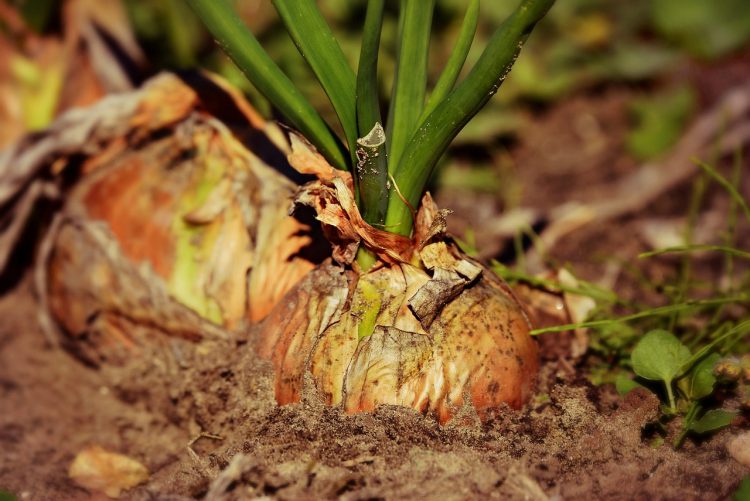
If you’ve ever dreamed of growing your own vegetables, herbs, or flowers but have felt intimidated by the process, you’re not alone. Many aspiring gardeners are held back by the idea that gardening requires a lot of expertise, space, or complicated techniques. The truth is, starting your own garden is far more approachable than you might think, and it can be a rewarding experience regardless of your level of expertise or available space. This guide will walk you through the basic steps to get you started on your first garden, demystifying the process so you can reap the rewards of a thriving garden.
Why Start a Garden?
Starting a garden offers countless benefits. Not only does it provide a sense of accomplishment, but it also gives you access to fresh, organic produce right in your backyard. Gardening is an activity that can reduce stress, improve mental health, and even provide a moderate form of physical exercise. The act of planting, nurturing, and eventually harvesting can bring joy to your daily routine. Whether your goal is to grow vibrant flowers to beautify your space or harvest fresh herbs and vegetables for your meals, the sense of satisfaction that comes from cultivating your own garden is unmatched.
Choosing the Right Location
One of the most important decisions you will make is choosing the location for your garden. The success of your plants depends heavily on the amount of sunlight they receive. Most vegetables and flowers need about 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight each day. Find a spot in your yard or on your balcony that has good sun exposure. If you’re growing in a smaller space, such as an apartment or urban environment, consider using window boxes or containers that can be moved to follow the sunlight throughout the day.
In addition to sunlight, consider accessibility. Choose a location that is easy to reach for watering and maintaining your plants. You are more likely to tend to your garden regularly if it is conveniently located, such as near a door or walkway.
Planning and Preparing the Soil
The foundation of any successful garden is healthy soil. Start by assessing the soil in your chosen location. If you are gardening in the ground, you may need to test the pH and nutrient levels of your soil to ensure it can support plant growth. Most plants thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, typically between 6.0 and 7.0. Testing kits are widely available, and using one can help you determine if your soil needs adjustments.
If your soil is lacking in nutrients, you can amend it by adding organic matter such as compost or manure. Compost is especially beneficial because it improves soil structure, moisture retention, and nutrient content. If you don’t have access to a garden bed, raised beds or container gardening are great alternatives. Raised beds allow you to control the soil quality and make it easier to manage pests and weeds. Container gardening, on the other hand, allows you to grow a variety of plants in small spaces.
Choosing What to Grow
For beginners, it’s best to start with plants that are easy to grow and maintain. Vegetables like tomatoes, lettuce, zucchini, and radishes are excellent choices for new gardeners because they grow quickly and don’t require much maintenance. Herbs such as basil, mint, and parsley are also beginner-friendly and can be easily grown in pots.
When selecting plants, take into consideration your climate, the time of year, and your specific preferences. Some plants, like lettuce and peas, thrive in cooler weather, while others, like peppers and tomatoes, require warmer temperatures. Make sure to read the plant tags or seed packets to understand their requirements. It’s also a good idea to start with seedlings rather than seeds, as they require less time and care in the early stages of growth.
Getting the Right Tools
You don’t need a lot of fancy equipment to start a garden, but a few basic tools will make the job easier and more enjoyable. A hand trowel, gardening gloves, a watering can or hose, and a pair of pruning shears are essential. If you are planting in the ground, a garden fork or spade can help with loosening and turning the soil. Invest in good quality tools that will last you for years, and keep them clean to avoid spreading diseases between plants.
Planting Your Garden
When it comes time to plant, make sure you follow the spacing recommendations for each type of plant. Crowding plants can lead to competition for nutrients, light, and water, resulting in poor growth. Dig a hole slightly larger than the root ball of your plant, gently place the plant in the hole, and fill it in with soil. For seeds, plant them at the depth recommended on the packet and gently cover them with soil.
Watering is crucial at this stage. Newly planted seeds and seedlings need consistent moisture, but be careful not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot. A good rule of thumb is to keep the soil moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around your plants can help retain moisture and suppress weeds, making maintenance easier for you.
Caring for Your Garden
Once your garden is planted, it’s time to focus on regular care. Watering, weeding, and fertilizing are essential to keeping your garden healthy. Water your garden in the early morning or late evening to reduce evaporation and give the plants time to absorb moisture. A drip irrigation system can make watering easier and more efficient, especially if you have a larger garden.
Weeds can quickly become a problem if left unchecked. Pull them out by hand or use a hoe to keep the soil weed-free. Adding a layer of mulch around your plants can also prevent weed growth and help retain soil moisture. Fertilizing your garden periodically will provide your plants with the nutrients they need to grow. Organic fertilizers, such as compost tea or fish emulsion, are great options for feeding your plants without using harsh chemicals.
Dealing with Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases are common challenges in gardening, but they don’t have to derail your efforts. Keeping a close eye on your plants will help you catch problems early. Signs of pests include chewed leaves, discoloration, and tiny holes, while diseases may manifest as spots on leaves or wilting. Consider using natural pest deterrents like insecticidal soap or neem oil, which are effective without harming beneficial insects.
Creating a garden that attracts beneficial insects such as ladybugs, bees, and lacewings can help control pest populations naturally. These insects prey on harmful pests and help with pollination. You can attract them by planting flowers like marigolds, calendula, and sunflowers among your vegetables.
Harvesting and Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor
Harvesting is one of the most rewarding parts of gardening. Knowing when and how to harvest your crops is important for ensuring the best flavor and quality. Vegetables like lettuce can be harvested by picking outer leaves while letting the inner part continue to grow. Tomatoes should be picked when they are fully colored and firm to the touch.
Regular harvesting not only gives you fresh produce but also encourages your plants to keep producing. Herbs can be harvested by pinching off the leaves, which also helps promote bushier growth. Once you’ve harvested your crops, enjoy them in your favorite recipes, share them with friends and family, or even preserve them through canning or drying to enjoy later.
Learning and Growing
Gardening is a continuous learning experience, and every gardener, no matter how experienced, encounters successes and setbacks. Don’t be discouraged if some of your plants don’t thrive as expected—gardening is all about experimenting and learning what works best for you and your environment. Keep a gardening journal to track your successes and challenges. Documenting what you plant, when you plant it, and how it performs will help you improve your gardening skills over time.
Starting your first garden might seem like a big challenge, but with patience and a bit of dedication, it can become a fulfilling and enjoyable part of your life. Each seed you plant is a step towards creating a green space that not only brings you closer to nature but also provides tangible rewards. So grab your gloves, pick a sunny spot, and start planting—your garden awaits!