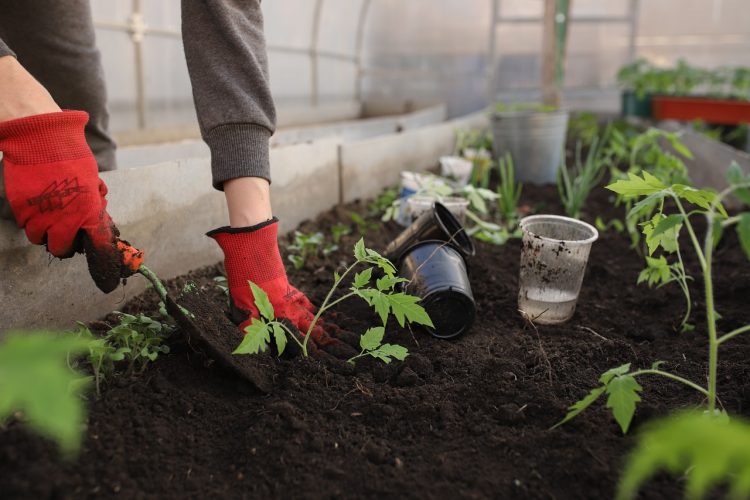
Growing your own vegetable garden can be an incredibly rewarding experience. It gives you the satisfaction of producing fresh, organic vegetables right from your backyard, offers a way to reduce your grocery bills, and promotes a healthier lifestyle. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or a beginner, cultivating a successful vegetable garden requires careful planning, preparation, and ongoing care. This guide will help you understand the key steps and tips to create a thriving vegetable garden that yields a bountiful harvest.
Choosing the Right Location
The first step to creating a thriving vegetable garden is selecting an ideal location. Vegetables need a lot of sunlight to grow properly, so choose a spot in your garden that gets at least six to eight hours of direct sunlight each day. Vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers are sun-loving plants that need plenty of light to produce abundant yields. A spot that is sheltered from strong winds and has well-draining soil is also essential for optimal plant growth.
If you don’t have much space, don’t worry. Many vegetables can be grown in containers or raised garden beds, allowing you to have a productive garden even if you live in an urban environment or have a small backyard. Containers are particularly useful because you can move them around to capture the best sunlight.
Preparing the Soil
Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful vegetable garden. Your soil should be rich in organic matter and have a good texture that allows roots to spread and grow easily. Before planting, prepare your soil by loosening it to improve aeration and drainage. You can do this by tilling or using a garden fork to break up compacted areas. Make sure to remove any large rocks, weeds, or debris.
Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to your soil is crucial to creating an environment where your vegetables can thrive. Compost helps improve the soil’s structure, retains moisture, and provides essential nutrients that your plants need to grow. Aim to work a few inches of compost into the top 6 to 8 inches of your soil. If you are using containers, make sure to use high-quality potting mix that includes organic material.
Deciding What to Plant
One of the joys of starting a vegetable garden is deciding what to plant. When choosing vegetables, consider your personal preferences as well as the local climate and growing conditions. If you are new to gardening, start with vegetables that are easy to grow, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, beans, lettuce, and radishes. These plants are forgiving, grow quickly, and produce abundant yields, making them perfect for beginners.
Take into account the seasonality of the vegetables you wish to plant. For instance, cool-season crops like carrots, peas, and spinach can be planted in early spring or fall, while warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, and squash do best when planted after the last frost in the spring. If you’re unsure what vegetables grow best in your area, consult a local gardening guide or nursery for advice.
Planting Your Garden
Planting is one of the most exciting stages of gardening. Once you have selected your vegetables and prepared the soil, it’s time to get planting. Make sure to space your plants according to the recommendations provided on the seed packet or plant tag. Proper spacing is essential to ensure your plants receive enough sunlight, nutrients, and airflow, which helps prevent disease.
If you are planting seeds, follow the recommended planting depth and spacing for each type of vegetable. For seedlings, dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the plant, place the plant in the hole, and gently fill it in with soil. Gently firm the soil around the base of the plant and water well after planting.
It’s also a good idea to plant flowers, such as marigolds or nasturtiums, alongside your vegetables. These companion plants can help deter pests, attract beneficial insects, and enhance pollination, ultimately contributing to a healthier and more productive garden.
Watering and Feeding
Proper watering is key to a thriving vegetable garden. Most vegetables need about an inch of water per week, but this can vary depending on the weather and type of soil. Water deeply and consistently to encourage the development of strong root systems. Avoid watering from above, as wet leaves can promote disease; instead, water at the base of the plant or use a soaker hose to deliver water directly to the roots.
In addition to watering, your vegetables will also benefit from periodic feeding. Fertilizing your garden provides your plants with the essential nutrients they need to grow. Organic fertilizers such as compost, fish emulsion, or bone meal are great options that will not harm the environment. Make sure to follow the recommended application rates for the fertilizers you use, as over-fertilizing can damage your plants.
Managing Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases are among the biggest challenges when growing a vegetable garden. A healthy garden with strong plants is less susceptible to pests, but you may still encounter problems along the way. Common garden pests include aphids, caterpillars, and beetles, while common diseases include blight, powdery mildew, and fungal infections.
To minimize the impact of pests and diseases, regularly inspect your plants for signs of trouble. Removing affected leaves, using insecticidal soap, or introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can help control pest populations. Planting a diverse range of vegetables and incorporating herbs and flowers can also deter pests and encourage natural predators.
Crop rotation is another effective strategy for minimizing the risk of disease. By rotating the placement of your crops each year, you can prevent soil-borne diseases and pests from becoming established. Try to avoid planting vegetables from the same family in the same spot year after year.
Weeding and Mulching
Weeds compete with your vegetables for nutrients, sunlight, and water, so keeping them under control is essential to creating a thriving garden. Hand-pulling weeds or using a hoe to remove them is effective, but the key is to stay consistent—removing weeds when they are small is much easier than dealing with larger ones that have established deep roots.
Mulching around your vegetable plants is a great way to suppress weeds, retain soil moisture, and improve soil quality. Organic mulch, such as straw, grass clippings, or shredded leaves, will eventually break down and add nutrients to the soil. Apply a layer of mulch around your plants, being careful not to place it directly against the stems, which could promote rotting.
Harvesting Your Vegetables
One of the most satisfying parts of gardening is harvesting the vegetables you’ve worked hard to grow. Knowing when and how to harvest your crops is crucial to enjoying the best flavor and quality. For example, lettuce and leafy greens can be harvested by picking the outer leaves as needed, while tomatoes should be picked when they are fully colored and slightly firm.
Harvesting regularly encourages your plants to keep producing. If you let vegetables like zucchini or cucumbers stay on the vine too long, the plant will slow down production. Check your garden daily to see which vegetables are ready to harvest, and enjoy them fresh in your favorite dishes.
Tips for Success
- Start Small: If you’re a beginner, it’s better to start small and gradually expand your garden as you gain experience. A small garden is easier to manage, and you can focus on learning about the plants you’re growing without feeling overwhelmed.
- Learn from Mistakes: Gardening is a learning process, and you may not succeed with every crop you plant. Don’t get discouraged if some of your vegetables don’t thrive—each season presents an opportunity to learn and improve your gardening skills.
- Keep Records: Keeping a gardening journal can help you track what works and what doesn’t. Record information about planting dates, weather conditions, pests, and harvest times to help guide your decisions in future seasons.
- Be Patient: Vegetables take time to grow, and patience is key to a thriving garden. While it may be tempting to rush the process, allowing your plants to mature at their own pace will yield the best results.
- Ask for Help: Don’t hesitate to seek advice from experienced gardeners or join a local gardening group. Gardening communities are often full of knowledgeable people who are eager to share their tips and experiences.
Creating a thriving vegetable garden is all about planning, preparation, and ongoing care. By selecting the right location, preparing your soil, choosing appropriate plants, and maintaining consistent care, you can enjoy a garden that produces fresh, delicious vegetables throughout the growing season. Gardening is a journey that is both rewarding and educational, and with time, you’ll find your own rhythm and joy in the process. Get your hands dirty, enjoy the sunshine, and start growing your own food—the results are worth it!